Effexor XR dosages: 150 mg, 75 mg, 37.5 mg
Effexor XR packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
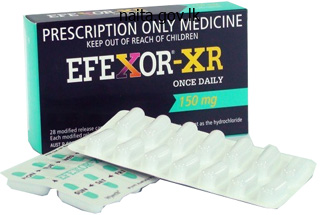
Purchase effexor xr canada
Invagination divides the roof of the fourth ventricle into an anterior and a posterior membranous space. Cerebellar vermian progress forces the posterior membranous space of the roof of the fourth ventricle to invaginate posteriorly beneath the vermis, ensuing in the Blake pouch. The median fenestration of the Blake pouch by the foramen of Magendie results in its subsequent disappearance. In 1% to 2% of wholesome subjects, the foramen of Magendie is absent; the communication between the fourth ventricle and the subarachnoid area is established when the foramina of Luschka open. The cerebellum seems as a butterfly-shaped structure shaped by the round cerebellar hemispheres joined in the middle by the marginally extra echogenic cerebellar vermis. The cerebellar hemispheres are well depicted on transverse and coronal images and are hypoechoic with a more echogenic lining. By the top of the second trimester, the elevated growth of the folia leads to an elevated echogenicity characterising the striped look. Two retrocerebellar septa, perpendicular to the cerebellum, could be visualised in a transverse view within the cisterna magna in the second and third trimesters in 84% to 92% of fetuses, respectively, and are considered to be remnants of the walls of the Blake pouch. Reliable interpretation of the traditional development and progress of the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis is possible from 18 weeks onwards. Posterior fossa malformations have recently been grouped because the Dandy-Walker continuum because of new insights in the embryologic improvement of this region. The sonographic categorisation of posterior fossa fluid collections depends on the assessment of the position of the torcular and the integrity of the cerebellar vermis. Pitfalls within the diagnosis of posterior fossa anomalies have been attributed to confusion in terminology describing vermian pathology, the gestational age at prognosis, the incorrect evaluation of the midsagittal plane of the cerebellum and the late improvement of some pathological conditions. In the second half of gestation, the anteroposterior diameter of the cisterna magna is stable and measures between 2 and 10 mm. The situation should be differentiated from the Dandy-Walker advanced, cerebellar hypoplasia and posterior fossa arachnoid cyst. Children with an enlarged cisterna magna are in danger for mild developmental delay. The place of the tentorium cerebelli is unbroken, but an upward and posterior rotation (<45 degrees) of a normally developed vermis with a traditional cisterna magna is characteristic of a Blake pouch cyst. The fluid content material of the Blake pouch cyst shows a more translucent echogenicity than that of the cisterna magna. The overall neurologic outcome of Blake pouch cyst is sweet as a outcome of the cerebellum and vermis have developed fully. In a retrospective evaluation of 19 instances of Blake pouch cyst, 10 fetuses introduced without associated malformations, 7 of which offered a traditional outcome. Nine instances of 19 showed extra malformations: 5 of 9 had a cardiac anomaly, 1 of which had trisomy 21. A, Axial view of the posterior fossa, revealing a cystic construction in affiliation with the cerebellum. B, Sagittal imaging permits simple differentiation kind other posterior fossa anomalies (asterisk signifies the upward-rotated vermis; � signifies Blake pouch). Associations with congenital heart defects, urinary tract anomalies and facial clefts have been described, usually in the context of chromosomal anomalies (50%�70% of the instances: T13, T18, T21, forty five,X) and genetic syndromes(WalkerWarburg syndrome, Aicardi syndrome, Neu-Laxova syndrome and Meckel-Gruber syndrome). Maternal diabetes, extreme alcohol consumption and early in utero an infection might predispose to the situation. On sagittal imaging, the vermis is absent or severely hypoplastic, rotated counterclockwise and positioned behind the quadrigeminal plate. The tentorium cerebelli is elevated by an infratentorial cyst rising the angle between the brainstem and tentorium to greater than forty degrees. Intellectual development is regular in 35% to 50% of the cases depending on the vermian improvement and absence of supratentorial malformations. Partial agenesis of the vermis with a normal or virtually normal lobulation, although difficult to consider because of the mass effect of the posterior fossa cyst, has a better prognosis. Cerebellar hypoplasia is characterised by a reduced cerebellar volume as a end result of the maldevelopment of 1 or each hemispheres and a small however normally formed vermis. This heterogeneous situation is associated with trisomies 9, 13 and 18, congenital issues of glycosylation, anticonvulsant medication (valproic acid) or cocaine. Typically, in unilateral cerebellar hypoplasia or aplasia, an uneven pons is current with contralateral volume reduction.
Diseases
- Venencie Powell Winkelmann syndrome
- M?nchausen syndrome by proxy
- Splenic agenesis syndrome
- Varicella zoster
- Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility type 5
- Lambert Eaton syndrome
- Typhus
- Hypolipoproteinemia
Order effexor xr line
Prevention of perinatal death and opposed perinatal outcome utilizing: a meta-analysis. Competing risks mannequin in early screening for preeclampsia by biophysical and biochemical markers. Prediction of small-for-gestation neonates from biophysical and biochemical markers at 11-13 weeks. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the American College of Medical Genetics. The influence of bias in MoM values on patient threat and screening performance for Down syndrome. Impact of bias in serum free beta-human chorionic gonadotropin and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-a multiples of the median ranges on first-trimester screening for trisomy 21. A mixture mannequin of nuchal translucency thickness in screening for chromosomal defects. About half of the congenital anomalies may be diagnosed within the late first trimester. Severe and infrequently lethal anomalies may be diagnosed, allowing mother and father the choices of constant with the being pregnant or, if acceptable, termination of being pregnant. Women appreciate the chance of early reassurance or early diagnosis, making this scan a vital first step in screening for congenital anomalies. The focus was initially on high-risk pregnancies6 but progressively prolonged towards extra unselected populations. What remains to be lacking is a consensus on when this investigation must be carried out (12�14 weeks), on the popular strategy (transabdominal or transvaginal) and how extended it ought to be. The fetal backbone, although not but utterly ossified, may additionally be observed along its complete extension from the cervical origin to the sacrum. By tilting the probe on either side of the fetal physique, the extremities are visualised along with the lengthy bones. A first trimester fetus has generally open arms, easily enabling counting of fingers. The legs are often flexed and the toes close to one another so that in a single sweep, their positions may be assessed. Cross-sectional planes from cranial to caudal present in the head the picture of the falx (midline) and of the choroid plexuses, filling at this stage almost entirely the relatively large lateral ventricles. More caudally, the fetal stomach is seen underneath the heart just above the extent of the umbilical wire insertion. Finally, lower in the pelvis, the bladder is seen, flanked by the two umbilical arteries. The kidneys can often be noticed as two extra echogenic oval constructions on either side of the backbone. This quick and gross anatomical survey allows exclusions of main and principally deadly structural anomalies such as acrania, exencephaly, holoprosencephaly, gross spinal anomalies, belly wall defects, megacystis and gross skeletal or limb deformities. Appreciation of the guts axis and of the fourchamber view and outflow tracts by colour Doppler excludes gross cardiac anomalies. In lean girls, this probe can provide glorious pictures, particularly of the fetal coronary heart. The largest examine to date, on 44,850 euploid fetuses examined on the time of the nuchal scan, confirmed that structural anomalies had been observed in 1. The authors state that about one-third of the structural anomalies are amenable to early analysis, and about 40% can potentially be detected within the first trimester. Arrays reveal in these fetuses a further 5% of pathological copy quantity variants. Early detection offers dad and mom the option to terminate the being pregnant at a stage when termination may be much less traumatic. Neurodevelopment begins from the neurulation part, from around 19 days of embryonic life to around day 26.
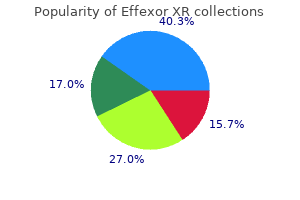
Purchase 75 mg effexor xr with visa
Perinatal and early surgical consequence for the fetus with hypoplastic left coronary heart syndrome: a 5-year single institutional expertise. The hypoplastic left heart syndrome with intact atrial septum: atrial morphology, pulmonary vascular histopathology and outcome. Diagnosis and management of proper ventricledependent coronary circulation in pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum. Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum: impression of fetal echocardiography on incidence at start and postnatal end result. Morphologic and practical predictors of eventual circulation in the fetus with pulmonary atresia or important pulmonary stenosis with intact septum. Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum: predictors of early and medium-term consequence in a population-based research. Spectrum of cardiovascular disease, accuracy of analysis, and end result in fetal heterotaxy syndrome. Diaphragmatic hernia: a postnatal complication of anomalous drainage of the umbilical vein. Prenatal prognosis of persistent left superior vena cava and its related congenital anomalies. Vasoreactive response to maternal hyperoxygenation in the fetus with hypoplastic left coronary heart syndrome. Long-term prognosis of double-switch operation for congenitally corrected transposition of the great arteries. Prenatal and postnatal survival of fetal Tetralogy of Fallot: a meta-analysis of perinatal outcomes and associated genetic problems. Common arterial trunk in the fetus: characteristics, associations, and outcome in a multicentre series of 23 instances. Truncus arteriosus: diagnostic accuracy, outcomes, and impact of prenatal prognosis. Anatomy of coarctation, hypoplastic and interrupted aortic arch: relevance to interventional/ surgical treatment. Ventricular discrepancy as a sonographic signal of coarctation of the fetal aorta: how reliable is it Coarctation of the aorta: lifelong surveillance is obligatory following surgical restore. Reversal of fetal ductal constriction after maternal restriction of polyphenol-rich meals: an open scientific trial. Nitric oxide and reactive species are modulated within the polyphenol-induced ductus arteriosus constriction in pregnant sheep. Identification of the one hundred richest dietary sources of polyphenols: an software of the Phenol-Explorer database. Premature foetal closure of the arterial duct: scientific presentations and consequence. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: morphology and end result from a world population-based study. The area behind the heart within the four-chamber view and the quest for congenital coronary heart defects. Doppler echocardiography within the prognosis and management of persistent fetal arrhythmias. Assessment of fetal atrioventricular time intervals by tissue Doppler and pulse Doppler echocardiography: normal values and correlation with fetal electrocardiography. Evaluation of fetal arrhythmias from simultaneous pulsed wave Doppler in pulmonary artery and vein. Diagnosis and remedy of fetal cardiac illness: a scientific assertion from the American Heart Association. Isolated atrioventricular block in the fetus: a retrospective, multinational, multicentre examine of a hundred seventy five sufferers. A limited variety of congenital malformations of the respiratory tract could be identified directly by prenatal sonography.

Buy discount effexor xr 150 mg
The look of surfactant in fetal air areas lags behind the buildup of surfactant in fetal lung tissue. The time period infant has a large excess of surfactant that facilitates speedy pulmonary adaptation to air respiratory. The amount of surfactant in the lung saccules in infants younger than 32 weeks and within the developing alveoli and small airways after 32 weeks is determined by the physiologic events experienced by the fetus or new child. With labor and the stress of supply, a few of the lamellar our bodies are secreted into the fetal lung fluid, and surfactant concentration will increase as fetal lung fluid quantity decreases. Similar measurements by Griese and colleagues73 yielded a surfactant pool measurement estimate of 20 mg/kg. Although not measured in humans, term newborn animals have surfactant swimming pools of roughly one hundred mg/kg. In contrast, the surfactant pool measurement within the grownup human is simply roughly four mg/kg. This inconsistency will be addressed relative to surfactant function later in this chapter. The curve for treatment with surfactant provides the dose-response curve for ventilated 27-day gestationrabbits. The changes in surfactant focus in airway samples will, partially, reflect pool sizes. For example, in sheep solely approximately 25% of the remedy dose is recovered 5 hours after treatment. In scientific research, surfactant parts labeled with stable isotopes have been used to evaluate surfactant metabolism in infants. Measurements of synthesis of surfactant phospholipids generally involve the intravascular injection of labeled precursors. Secretion may be measured by recovering the labeled surfactant elements from the air spaces, which evaluates the overall kinetics of synthesis and secretion. After term delivery and air flow of lambs, an intravascular injection of radiolabeled palmitic acid is included into lung phosphatidylcholine inside minutes. Subsequent surfactant therapy of these preterm lambs brought on a large dilution of the endogenous surfactant. The curve for preterm baboons has a longer delay in detection than the curve for preterm sheep as a result of the radiolabel was not given as a pulse label and time was required to get sufficient label into the air area to be detected. Little surfactant is misplaced from grownup lungs to the lymph or vascular area unless the lung is injured, and minimal quantities of surfactant are lost by suctioning the airways, except edema fluid is current. In the time period lamb, a hint dose of surfactant given at delivery had a half-life of roughly 6 days, which is longer than values of approximately 10 hours for adult animals. The share of a remedy dose of surfactant that was lost from the air spaces was related with high tidal volume air flow or with high-frequency oscillatory air flow in preterm lambs. No data is available in the preterm about where degradation of surfactant happens. The normal preterm lung at delivery accommodates few macrophages and primarily no granulocytes. However, irritation and damage will quickly recruit inflammatory cells to the lung, which can then increase the lack of surfactant. The solely practical measurement of surfactant pool size and biological half-life within the human is to give a hint or remedy dose of surfactant containing a secure isotope and to follow the change in focus of the label within the surfactant sampled by aspiration of the air areas. This measurement provides an built-in evaluation of the mixing of the exogenous label with the endogenous air house surfactant and tissue swimming pools of surfactant. However, impartial data from preterm lambs and baboons indicate that only approximately 20% of the surfactant would have been in the air spaces at 24 hours, and 25% of the surfactant would have been lost from the lung compartment. Tubular myelin and other free surfactant lipoprotein arrays within the hypophase generate the surface film within the alveolus and small airways. New surfactant enters the floor movie and "used" surfactant leaves as small vesicles, which then are cleared from the air areas.
Silver Lime (Linden). Effexor XR.
- Sleep disorders, headaches including migraines, incontinence, excessive bleeding (hemorrhage), itchy skin, painful swelling of joints (rheumatism), bronchitis, cough, spasms, fluid retention, inducing sweating, and other conditions.
- What is Linden?
- Dosing considerations for Linden.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Linden work?
Source: https://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96550
Discount effexor xr generic
Maternal Disease the most typical maternal situations that can result in fetal musculoskeletal anomalies (Table 34. Poorly controlled, insulin-dependent diabetes is the most typical maternal condition that can lead to significant skeletal anomalies in fetuses, which embody developmental field defects of the spine, vertebral segmentation defects, caudal regression syndrome and deficiencies of the limbs (particularly femoral hypoplasia, tibial hemimelia, preaxial hallucal polydactyly) in addition to anomalies of other viscera, in particular the center and urogenital tract. In maternal myasthenia gravis, transmission of acetylcholine receptor antibodies to the fetus may find yourself in generalised arthrogryposis and neonatal or infant dying. Careful examination of the the rest of the fetal anatomy can reveal additional signs of a skeletal dysplasia (Table 34. The cranium ought to usually be rugby ball in shape and cast a great acoustic shadow, indicating regular mineralisation. In circumstances related to hypomineralisation in later pregnancy, the skull shape can readily be deformed by pressure from the transducer. Affected neonates are very floppy and infrequently have respiratory problems requiring ventilatory help, and the mortality fee is high (20%). Most survivors have vital developmental delay and a lowered life expectancy. The finding of talipes and polyhydramnios in a euploid fetus should prompt examination of the mom for signs of myotonic dystrophy. An axial view of the palate should be visualised to find a way to detect significant levels of cleft palate, which may be associated with several dysplasias. A sagittal view will reveal micrognathia, flattening of the facial profile, frontal bossing or a depressed nasal bridge. Measurement of the mandible and orbital diameters may be helpful but may be more difficult to obtain in later being pregnant with rising acoustic shadowing from surrounding bony structures. Length of lengthy bones should be checked towards acceptable charts of lengthy bones length. It may be extra marked within the proximal lengthy bones (rhizomelia) or the forearms and decrease legs (mesomelia). Deformity; hypoplasia; or absence of tibia, fibula, radius or ulna could also be current. The ends of the bones ought to be fastidiously examined to exclude epiphyseal stippling that may indicate a chondrodysplasia punctata. C, Coronal view of a backbone in a fetus with brachytelephalangic chondrodysplasia punctata. D, Radiograph showing lateral view of the spine on this neonate with brachytelephalangic chondrodysplasia punctata. The joints may be irregular in a variety of skeletal, neurologic and neuromuscular situations in addition to a heterogeneous group of hereditary distal arthrogryposes. However, some skeletal dysplasias have hypoplastic clavicles (cleidocranial dysostosis, pycnodysostosis) or scapulae (camptomelic dysplasia). Nomograms of thoracic circumference are available, but a small chest can often be identified by remark alone. A, Ultrasound image of preaxial polydactyly of the ft in Greig acrocephalopolysyndactyly. C, Ultrasound image showing the syndactyly ensuing within the mitten hand seen in Apert syndrome. The chest can be small secondary to a short backbone, as in some of the spondylodysplasias. The ribs themselves must be examined fastidiously as they may be brief, thick, skinny, beaded or irregular in organisation or number. The remainder of the fetal anatomy must be examined fastidiously because many skeletal dysplasias and genetic syndromes characterised by skeletal anomalies can have abnormalities of the urogenital tract, heart and brain (see Table 34. Indeed, the scientific presentation of some dysplasias is such that sonographic findings may not be evident until later in pregnancy. Furthermore, with increasing data of the underlying molecular pathology, identification of markers of skeletal dysplasias can permit for focused invasive or more and more noninvasive9 diagnosis for definitive assessment of prognosis to inform parental counselling and subsequent pregnancy management. Both situations have a flat nasal bridge with a short nostril and anteverted nostrils. Sonographically and radiologically, ossification of the skull, spine and pelvis is more deficient in kind 1 than in type 2. The lengthy bones are shorter in type 1, which has been subdivided into sorts 1A (Houston-Harris) and 1B (Parenti-Fraccaro).
150 mg effexor xr purchase free shipping
True mosaicism may reflect two completely different situations: generalised mosaicism or confined placental mosaicism. Generalised mosaicism is when the abnormality is found in both the fetus (true fetal mosaicism) and the placenta, and confined placental mosaicism is when the abnormality is absent from the fetus but discovered within the extraembryonic tissues. The likelihood of being confirmed within the fetus on the time of amniocentesis also differs depending on the precise chromosome involved. Rare autosomal mosaic trisomies that symbolize true fetal mosaicism usually tend to be related to structural fetal anomalies, and roughly 12. Confined placental mosaicism of trisomy 16 is believed to trigger poor placental perform, resulting in intrauterine development restriction of the fetus and preeclampsia in the mom, typically resulting in pregnancy issues and preterm start. An extra caveat is that certain chromosomal abnormalities are noticed in solely a single tissue or pattern kind. For phenotype�genotype correlation, in each classical and molecular cytogenetics, you will need to keep in mind that sufferers within the postnatal setting are often ascertained due to clinical features associated to their genetic condition. Chromosomal imbalances seen on karyotype are often absolutely penetrant due to adjustments in a lot of genes. Therefore if the same finding is seen in a standard father or mother, the prognosis is usually good for the fetus. The evaluation involves measuring the exact number of repeats at a quantity of loci in both the fetus and the mom to decide the allele sizes in every. If tradition failure happens, patients are provided a repeat process for cytogenetic or microarray evaluation. Concluding Remarks Prenatal cytogenetic analysis has undergone vital developments since it started more than 50 years in the past. The focus of cytogenetic prenatal testing has primarily been aneuploidy given the elevated threat for chromosomal anomalies related to maternal age. However, current advances in diagnostic testing now permit for the detection of submicroscopic abnormalities that appear to be age unbiased. Despite the advances in know-how, detection of low-level mosaicism and lack of highresolution breakpoint information in apparently balanced de novo cytogenetic aberrations stay challenges in clinical cytogenomic testing. These points are being addressed with the introduction of next technology sequencing-based assays into the realm of prenatal analysis. Current investigations of sequencing know-how are aimed at assessing their diagnostic worth and medical utility during pregnancy. Such enhancements will doubtless pave the way in which for a comprehensive copy quantity and sequence-based genetic testing option throughout being pregnant by means of routine fetal sequencing. Culture Failure Prenatal specimens must be arrange and monitored with care to avoid culture failure. Although the speed of culture failure is generally low, it varies from laboratory to laboratory. Factors that contribute to the success of prenatal cultures embrace the size of the pattern and the gestational age. Amniocentesis samples from pregnancies at a sophisticated gestational age also have elevated failure rates because of the big number of nonviable cells present in the amniotic fluid. Method of sampling chorionic villi in first trimester of being pregnant beneath steering of real time ultrasound. Chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis: recommendations for prenatal counseling. Complications of diagnostic ultrasoundguided percutaneous umbilical blood sampling: analysis of a sequence of 341 cases and evaluation of the literature. Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling: outcomes from a multicenter collaborative registry. Prenatal diagnosis procedures and techniques to obtain a diagnostic fetal specimen or tissue: maternal and fetal dangers and benefits. Expanding the scope of noninvasive prenatal testing: detection of fetal microdeletion syndromes. Presymptomatic identification of cancers in pregnant women throughout noninvasive prenatal testing. Discordant noninvasive prenatal testing leads to a affected person subsequently diagnosed with metastatic disease.
Effexor xr 37.5 mg buy free shipping
Zagariya A, Doherty J, Bhat R, et al: Elevated immunoreactive endothelin-1 ranges in newborn rabbit lungs after meconium aspiration. Yigit S, Tekinalp G, Oran O, et al: Endothelin 1 concentrations in infants with meconium stained amniotic fluid. Robertson B: Anastomoses in the human lung: postnatal formation and obliteration of arterial anastomoses within the human lung: a microangiographic and histologic examine. Chinese Collab: Chinese Collaborative Study Group for Neonatal Respiratory Diseases. Patients sometimes present with respiratory distress shortly after delivery with or with out proof of pulmonary hypertension. Extrapulmonary manifestations embrace cardiac dysfunction, shock, neonatal ischemic encephalopathy, and in rare instances multiorgan failure. Management is supportive and contains mechanical ventilation for respiratory failure, surfactant replacement, antibiotics, hemodynamic support with inotropes, and screening for neonatal ischemic encephalopathy and multiorgan failure. Yeh T: Core ideas: meconium aspiration syndrome: pathogenesis and present administration. Sienko A, Altshuler G: Meconium-induced umbilical vascular necrosis in abortuses and fetuses: a histopathologic study for cytokines. Yamada T, Minakami H, Matsubara S, et al: Meconium-stained amniotic fluid displays chemotactic exercise for polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vitro. Vidyasagar D, Zagariya A: Studies of meconium-induced lung harm: inflammatory cytokine expression and apoptosis. Galambos C, Sims-Lucas S, Ali N, et al: Intrapulmonary vascular shunt pathways in alveolar capillary dysplasia with misalignment of pulmonary veins. Treatment of extreme meconium aspiration with porcine surfactant: a multicentre, randomized, controlled trial. Maturana A, Torres-Pereyra J, Salinas R, et al, the Chile Surf Group: A randomized trial of natural surfactant for moderate to extreme meconium aspiration syndrome. Bae C, Takahashi A, Chida S, Sasaki M: Morphology and performance of pulmonary surfactant inhibited by meconium. This resulted in a pathologic picture characterised by emphysema, fibrosis, and marked airway epithelial modifications. This has resulted in additional premature infants surviving with lungs at the late canalicular or early saccular section of improvement exposed to various antenatal and postnatal components that may disrupt normal alveolar and vascular development. These results recommend that, though positive airway stress and oxygen exposure at low levels should still be adequate to harm the immature lung, different elements additionally play an essential position within the improvement of milder lung damage. An improve in elastase and an imbalance between elastase and 1 proteinase inhibitor in the lung has also been postulated as a potential mechanism for the development of neonatal lung damage. A vicious circle is thereby created by which the required treatment for the respiratory failure, mechanical ventilation, and increased impressed oxygen induces more lung damage and exacerbates the respiratory impairment. The degree of abnormality in lung operate might vary from mild to severe, paralleling the scientific and radiographic presentation. Forcomparison,curvefornormalinfants(red line)andits 95% confidence limits (dashed lines) are proven. The injury to the small airways produces different time constants in different areas of the lungs, thereby altering the distribution of the inspired fuel. This decrease might mirror adjustments within the elastic properties of the lung secondary to fibrosis and interstitial fluid accumulation. Overdistention of parts of the lung from fuel trapping can further contribute to the lower in compliance. This can result in extreme maldistribution of the impressed gasoline,72 lung overdistention from fuel trapping, and hypoventilation with hypercapnia secondary to increased work of breathing. The mechanisms for increased airway resistance embrace several components that contribute to airway injury and obstruction. In addition, clearance of mucus could also be decreased on account of despair of ciliary activity. These episodes could be ameliorated by sedation or by sustaining a relatively excessive optimistic end-expiratory airway stress. Cold air or methacholine problem additionally produces a marked improve in pulmonary resistance in these patients. This hypoxemia is due mainly to a reduced ventilation-perfusion ratio and alveolar hypoventilation. The persistent hypercapnia is usually accompanied by a rise in serum bicarbonate concentration that compensates for the respiratory acidosis.

Order effexor xr toronto
The distal proper subclavian artery and all the left subclavian artery derive from the seventh intersegmental arteries (yellow). The pulmonary arteries and arterial duct derive from the sixth aortic arch arteries (blue). The the rest of the descending aorta (uncoloured) derives from the left dorsal aorta. The normal right subclavian artery develops from the connection of the seventh intersegmental artery with the proper fourth arch artery. Instead the seventh proper intersegmental artery takes origin from the right dorsal aorta. In this photograph, the thoracic contents are seen from behind, and the right subclavian artery is seen to take origin from the descending aorta on the left aspect and to run behind the oesophagus to attain its regular location. A series of ventral branches that provide the gut derivatives derived from a community of vitelline arteries 2. Lateral branches that supply retroperitoneal buildings corresponding to adrenals, kidneys and gonads 3. The segments of dorsal aorta connecting arches 3 and 4 regress, leaving the third aortic arch to supply blood to the head. The fourth and sixth arches endure asymmetrical remodelling to provide the upper extremities, dorsal aorta and lungs. The left fourth arch becomes the aortic arch between the left frequent carotid and left subclavian arteries and probably the most cranial part of the descending aorta. The right and left subclavian arteries derive from the seventh intersegmental arteries. The sixth arch arteries provide the pulmonary arteries, and the left arch offers the arterial duct. The ascending aorta provides rise to left and proper widespread carotid arteries and the best subclavian artery. It then arches over the hilum of the proper lung, and the descending aorta lies on the best side. The pulmonary trunk offers rise to the proper and left pulmonary arteries, with a left-sided arterial duct connecting the left subclavian artery to the left pulmonary artery. The left subclavian artery arises from the descending aorta by way of a socalled retro-oesophageal diverticulum (diverticulum of Kommerell). There is thus a complete vascular ring which surrounds the trachea and oesophagus; viewed posteriorly, the vessels display a Y-configuration formed by the aortic arch on the best and the left subclavian artery or diverticulum of Kommerell on the left. The descending thoracic aorta more distally is located within the midline, posterior to the oesophagus. No right-sided arterial duct was recognized, and there was no evidence of coarctation. There is a right aortic arch with right-sided aorta but a left arterial duct and an isolated left subclavian artery. The aorta gives rise to brachiocephalic and left common carotid arteries, but the aortic isthmus is absent (asterisk), and the descending aorta and left subclavian artery are supplied from the pulmonary trunk via the arterial duct. Conclusion the human coronary heart develops over a 4-week period from a mass of mesenchymal cells within the ventral embryo. An endothelial-lined tube enveloped by muscle types first and begins rhythmic contraction. The tube loops to the best, and from its partitions, the atrial and ventricular chambers balloon out. The conduction system develops from the primitive myocardium of the original coronary heart tube. A complex collection of arteries and veins develops sequentially and remodels to kind the definitive arterial and venous system. Secondary haemodynamic adjustments can greatly modify and exacerbate the original defect.

Discount 150 mg effexor xr
However, in addition, morphological changes may also occur indicating reduced fetoplacental circulate in the absence of any maternal abnormalities. Such adjustments include both the direct documentation of chorionic vascular thrombosis or the downstream villous effects of proximal fetovascular occlusion, namely clusters of chorionic villi with regular intervillous area exhibiting intravascular karyorrhexis, syncytial knot formation and stromal sclerosis, in accordance with chronicity. Contrast with bedside ultrasound findings in acute abruption in a labour and supply setting (D). Most instances of distal villous hypoplasia and villous hypermaturity are actually believed to be adjustments secondary to alterations in uteroplacental flow, though it has been advised that some may represent main maldevelopment. Inflammation affecting the fetal membranes overlying the cervical os, with subsequent spread to contain the membranes extra diffusely, the amniotic cavity and finally the fetal circulation, represents an infective course of, most often with normal vaginal or cervical commensal organisms, the condition representing a lack of regular steadiness between defence mechanisms and colonisation. Ascending genital tract infection is due to this fact a major cause of midtrimester pregnancy loss and severe preterm supply and even at term may act synergistically with different insults, corresponding to hypoxiaischaemia, to cause neurological harm. Because maternal blood supplies the intervillous house, maternal systemic diseases might involve the placenta, leading to either collections of inflammatory cells or fibrin throughout the intervillous Villitis or intervillositis attributable to haematogenous an infection. Abnormalities Primarily Affecting the Intervillous Space In addition to the maternal and fetal circulations, abnormalities affecting the traditional structure or perform of the intervillous house are rare however could occur and have distinctive histologic options. The aetiology is unknown but is presumed autoimmune, significantly in view of the findings that presentation could additionally be throughout pregnancy, from first trimester loss via to time period, with a higher than 50% recurrence risk. Amniocentesis revealed triploidy (partial hydatidiform mole), and the being pregnant was terminated by induction of labour. The pattern of tissue involvement might recommend a particular organism because the aetiology, however affirmation ought to at all times be based mostly on extra ancillary investigations. In some instances of viral infection, characteristic viral mobile inclusions may be current, making the precise prognosis extra definitive. As famous earlier, in some cases, the sample of irritation may be attribute and the aetiology determined to be an infectious agent. Such lesions are most frequently situated beneath the chorionic plate, may be single or multiple, and may range in dimension from millimetres to greater than 10 cm in diameter. Very not often, a spotlight of intraplacental choriocarcinoma may develop within an in any other case unremarkable third trimester placenta, which can result in metastatic illness of the mother, fetus or each. Tumours and Tumourlike Lesions There are few mass lesions affecting the placenta, but there are a quantity of entities which may be detected on antenatal sonographic examination, which have clear histologic correlates and effects on medical management. Typically, such instances show a sonographically homogeneously enlarged placenta with diffusely scattered hydropic cystic change in association with an apparently structurally normal fetus. Histologically, such placentas demonstrate characteristic hydropic change of stem villi, without trophoblast hyperplasia, usually in affiliation with marked dilation of chorionic plate vessels. Examples are the exact geographical localisation of sampling, in relation to the periphery, basal and chorionic plates, and twine insertion; the timing of sampling in relation to delivery; the mode of delivery; the strategy of protein extraction; and the temperature of storage and size of storage time. All these, and likely many but unrecognised, factors require modifications of current placental examination protocols, but such a multidimensional strategy will result in exciting new discoveries in relation to a variety of placental associated obstetric issues. Conclusion Many pregnancy issues are brought on by quite a lot of placental pathologies, a few of that are detectable antenatally through ultrasound examination. Histopathological examination of the delivered placenta might permit both affirmation of specific diagnoses and identification and mechanisms of underlying disease patterns and pathophysiology. Some pathological circumstances appear to be poorly detectable antenatally and, at current, are only recognised on microscopic placental examination. It is extremely likely that along with these abnormalities described, a variety of placental practical disorders may also lead to pregnancy issues, and in this context, the development of novel additional investigations may enable extra accurate detection of those problems and probably their early antenatal detection and prevention. Future Approaches To date, placental pathology information has been virtually exclusively based mostly on findings of subjective morphological research describing the frequency of varied histologic lesions in particular groups. Although this strategy has led to important observations associated to both scientific care and underlying mechanisms of disease, further developments are likely to require additional approaches which offer objective knowledge to minimise the results of nonblinding, unconscious bias and may establish mechanistic somewhat than structural alterations. Recent technological developments in -omic approaches, such as genomics, proteomics, metabolomics and microbiomics, may have profound results on the evaluation of tissue samples in disease, and such techniques are actually being applied to the placenta, and their findings are beginning to problem our current paradigms of illness mechanisms and pathophysiology. Practice guideline for examination of the placenta: developed by the Placental Pathology Practice Guideline Development Task Force of the College of American Pathologists. Two-dimensional sonographic assessment of maximum placental length and thickness in 12.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Effexor XR
Karrypto, 40 years: Brodersen R: Bilirubin: solubility and interaction with albumin and phospholipids. This is secondary energetic transport, which permits cells to move solutes against focus gradients and thus to management their surroundings more subtly than if diffusion gradients had been the only forces current. By distinction, spiral artery thrombosis and villous infarction are sometimes discovered on the margins of the placental disc after a term delivery, with no apparent unwell results. Meconium also incorporates blood group-specific glycoproteins and a small amount of lipid and protein that decreases throughout gestation.
Irmak, 41 years: Technique of Amniocentesis After a thorough ultrasonographic examination, a needle insertion site is selected. By this time, more than half of fetuses may demonstrate some degree of hypoxemia based upon percutaneous umbilical vein sampling and by wire blood gas measurements. Conclusion Examination after dying remains necessary in certain circumstances for guiding the administration of future pregnancies and as a means of medical audit and governance. Airway irritation results in elevated mucus manufacturing in addition to narrowing of the caliber of the airways.
Cruz, 56 years: Zhang H, Zheng W, Shen Y, et al: Experimental evidence exhibiting that no mitotically energetic feminine germline progenitors exist in postnatal mouse ovaries. This discovering probably displays a later maturation of the neuroregulatory system that controls heart fee variability. These shall be selected for feminine profit and thus might act to prohibit fetal development and reduce the demand on the mom, in accordance with the fetal-maternal battle speculation. The chance of a microbial breach of the cutaneous barrier rises within the presence of intravenous catheters, that are important for crucial care.
Gancka, 37 years: In fetuses, congenital heart disease continues to represent a standard indication for termination of being pregnant. Immunocytochemical reactivities and histochemical stains have significantly enhanced the microscopic observations of anatomic maturation, significantly in documenting synaptogenesis within the olfactory bulb, the maturation of particular person neuronal varieties, and the distribution of progenitor "stem" cells throughout the olfactory bulb. During bradycardia, filling quantity of the center could improve, resulting in a rise in stroke quantity and pulse strain in accordance with the Starling law. More than half of those very preterm infants may have serious developmental problems in cognitive, language, behavioral, sensory, or motor domains.
Miguel, 29 years: Associated anomalies � Pulmonary hypoplasia and atresia are frequent, and CoA is current in most fetuses with ventriculoarterial discordance (20%). Evidence that a practical neuromuscular interaction is concerned within the regulation of naturally occurring cell demise and the stabilization of synapses. Quantitative evaluation of placental perfusion by contrast-enhanced ultrasound in macaques and human subjects. Although the mechanistic details of malformations in human beings associated with exposures are incompletely understood, we anticipate that developments in the genetic basis of malformations and in cell biology will lead to our improved understanding of exposure-associated malformations.
Einar, 36 years: Arad-Cohen N, Cohen A, Tirosh E: the relationship between gastroesophageal reflux and apnea in infants. In neonates, application of constructive pressure also can trigger airway deformation and lead to extreme central airway collapse. Buscetta M, Papasergi S, Firon A, et al: FbsC, a novel fibrinogen-binding protein, promotes Streptococcus agalactiae-host cell interactions. Additionally, altered cortical activation and functional connectivity during language and visual processing is clear in children and adults born preterm, even amongst those with normal neurocognitive perform.
Sugut, 50 years: De novo balanced chromosome rearrangements and extra marker chromosomes recognized at prenatal diagnosis: clinical significance and distribution of breakpoints. The center layers contain myoid cells that have fibroblastic traits and assist create the blood-testis barrier. However, pregnant or breastfeeding women ought to keep away from fish recognized to have greater mercury content. Evidence that a practical neuromuscular interaction is involved in the regulation of naturally occurring cell demise and the stabilization of synapses.
Ines, 65 years: Koopman P, Gubbay J, Vivian N, et al: Male growth of chromosomally feminine mice transgenic for Sry. Mulrooney N, et al: Surfactant and physiologic responses of preterm lambs to steady optimistic airway strain. These infants are macrosomic and often show proof of congenital hyperinsulinism. In Neonatal and Fetal Medicine-Physiology and Pathophysiology, R Pollin, W Fox (eds.
10 of 10 - Review by D. Avogadro
Votes: 345 votes
Total customer reviews: 345
References
- Chalasani N, Baluyut A, Ismail A, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis: a multicenter case-control study. Hepatology. 2000;31:7-11.
- Kramer JM, Newby LK, Chang WC, et al. International variation in the use of evidencebased medicines for acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J 2003;24(23):2133-2141.
- Lloyd RV, Kloppel G, Rosai J, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2017.
- Granfeldt Ostgard LS, Medeiros BC, Sengelov H, et al. Epidemiology and clinical significance of secondary and therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia: a national population-based cohort study. J Clin Oncol 2015;33(31):3641- 3649.
- Gravenstein JS, Cooper JB, Orkin FK: Work and rest cycles in anesthesia practice, Anesthesiology 72:737-742, 1990.
- Kellogg ND, Menard SW, Santos A: Genital anatomy in pregnant adolescents: 'normal' does not mean 'nothing happened.' Pediatrics 113: e67-e69, 2004.
- Dunn R, Maclean A. General gastroenterology. In: Dunn R, et al, editors. The emergency medicine manual, 5th ed. Adelaide: Venom Publishing; 2010.